What is Arginine and how does it work in the body?
Arginine (symbol Arg or R), is an amino acid used by the body for the biosynthesis of proteins.
The Levogyra form, known as L-arginine, is considered an amino acid semi-essential or conditionally essential for its role in maintaining the homeostasis (condition of internal stability) of the organism according to the stage of development and state of health.
L-arginine is in fact nutritionally indispensable for infants (especially preterm infants) and in the early stages of life as they are unable to synthesize it. With growth, starting from 13-14 years and in optimal health conditions, this amino acid is no longer essential as it is easily integrated with the diet, being present in large quantities in all foods containing proteins.
It was first isolated in 1886 by German chemists Schultz and Steiger from lupine seeds. They called it by the Greek name argiros what does it mean "silver" due to its white-silvery crystal appearance.
Arginine can also be synthesized in the body through citrulline, another semi-essential amino acid. Conversely, also citrulline can be generated starting from arginine as both are involved in the reactions of the urea cycle, essential for eliminating ammonia (toxic to humans), in the form of urea, in the urine.
Curiously, the urea cycle is also known as the OCA cycle since the key amino acids are: ORrnitin, C.itrullina e TOrginina.
The importance of arginine revolves around the production of nitric oxide (NO), a key molecule for the functioning of the cardiovascular system whose identification earned the Nobel Prize for medicine in 1988 to the chemist Louis Ignarro, the American son of Italian emigrants.
This discovery initiated the development of cardiovascular drugs that induce the production of NO in blood vessels, dilating the arteries and thus preventing the formation of atherosclerotic plaques and clots.
In the brain, arginine is involved in cellular communication through neurotransmitters.
In addition to the detoxifying action of ammonia, the amino acid also intervenes in the biochemical processes of synthesis of proteins, sugars and complex molecules such as hemoglobin, insulin, collagen, elastin and creatine. Finally, at high doses it is capable of burning fat and stimulating the synthesis of muscle tissue as well as promoting the regeneration of liver tissue.
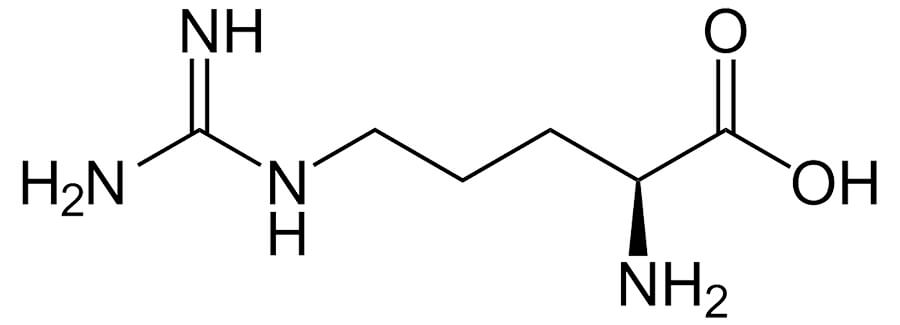
Chemical formula
Figure 1: Chemical structure of L-Arginine
Arginine is a basic alpha (α) amino acid with a hydrophilic polar side chain, present in proteins in the L configuration. Its brute or molecular formula is the following: C.6H.14No.4OR2 (C = carbon; H = hydrogen; N = nitrogen; O = oxygen).
The word "alpha" indicates the carbon atom (highlighted in the green box in Figure 1) to which a carboxylic group (-COOH) is bonded. In the structure of amino acids, 4 different groups are bonded to the alpha carbon (the -COOH, the amino group NH2, a hydrogen atom H and the side chain that confers certain properties).
The basicity is given by the presence of 2 amino groups (NH2) in the guanidine group of the side chain (red box in Figure 1).
This characteristic, together with the polarity, confers hydrophilicity to arginine. Amino acids with these properties therefore have affinity for aqueous environments and will be found in the outer portions of proteins.
Based on the arrangement of the groups around the alpha carbon, the amino acids can assume two different spatial configurations, each mirroring the other (like a pair of gloves or shoes): D. (Dextro) e L (Levorotation).
Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins and in nature, most of the proteins synthesized by living organisms are made up of L-amino acids.
Some D-amino acids have been found in the protein structure of deep-sea organisms, in the cell walls of bacteria and in the venom of some molluscs; moreover, few D-amino acids are also found in the neurons of the mammalian brain (including humans) and seem to play a role in the processes of neurotransmission and neurodegeneration.
Where is arginine found?
A healthy individual with a healthy and varied diet normally takes 3.5-5 grams (3500-5000mg; milligrams) of arginine per day, especially through meat, legumes, nuts and in general all foods rich in proteins.
It is interesting to note that through the consumption of the reference dose of 100 grams of the foods listed in Table 1, you can take the following doses of arginine (mg):
| CONTENT OF ARGININE IN FOODS | |
| FOOD | mg / 100g |
| Egg white powder | 4400 |
| Salted cod | 3750 |
| Walnuts | 3620 |
| Roasted peanuts (unsalted) | 3736 |
| Soy flour | 2670 |
| Cooked pork belly | 2500 |
| Toasted almonds | 2460 |
| Toasted hazelnuts | 2220 |
| Broad beans, chickpeas, lentils, dried soybeans | 2000-2200 |
| Meat | 1500-2000 |
| Roast turkey | 1980 |
| Cooked shellfish (lobsters and prawns) | 1640-1830 |
| Anchovies in oil | 1730 |
| Caviar | 1590 |
| Fish | 900-1200 |
| Whole egg (fresh) | 790 |
| Egg white (fresh) | 576 |
| Yolk (fresh) | 1131 |
| Cheeses | 540 |
| Cereals and derivatives (pasta, bread, rice ...) | 400-500 |
Table 1. Average arginine content (mg) per 100g of product
For healthy adults, who do not need to synthesize large quantities of arginine, that produced through the urea cycle and that supplemented through the diet is sufficient.
Arginine deficiencies are found in people who follow a strict, strictly vegetarian or vegan diet but also in situations of strong psychophysical stress, trauma (such as extensive burns) and in some pathological conditions. In these cases, L-methionine supplements are a valuable aid.
What are the benefits of arginine?
Research has identified the following benefits associated with arginine:
- Anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties: as already mentioned in the initial paragraph, arginine contributes to the elimination of toxins (ammonia) and free radicals responsible for inflammation and aging. It is often given in combination with other antioxidants, especially vitamin C and omega 3 as an antiaging. Due to its ability to eliminate ammonia through the urine, arginine is often used in people with metabolic problems and damage to the urethra. In fact, if ammonia persists in these areas, it can break down proteins and cause tissue necrosis with consequent chronic inflammation.
- Protection of the cardiovascular system: Individuals at risk of cardiovascular disease may have low levels of arginine, therefore cardiologists often prescribe supplements based on this amino acid to reduce the formation of atherosclerotic plaques and to prevent a heart attack or stroke. Arginine in fact exerts an antihypertensive effect by improving blood flow in patients suffering from coronary heart disease. It also contributes to the reduction of bad cholesterol (LDL) and triglycerides by relieving the symptoms of congestive heart failure associated with reduced blood flow from the heart to the limbs. It is commonly used in case of chest pain (angina pectoris) thanks to the antithrombotic effects of NO.
- Wound healingPeople with arginine deficiency have slow healing and healing of wounds and trauma due to reduced collagen deposition at injury sites. Arginine is often used together with topical creams and ointments for wound dressing as it induces the secretion of hormones (including growth hormone, GH) involved in the healing process. Thanks to the improvement of blood flow on the injured part and to the production of L-proline, it also increases the synthesis of collagen necessary for the repair and restoration of tissue function, accelerating healing. This is particularly useful in the treatment of severe burns, also reducing swelling and pain.
- Support in the treatment of impotence and erectile dysfunction in men and male and female infertility: being able to increase blood flow, arginine is often used in the treatment of erectile dysfunction (ED), also improving the production and motility of spermatozoa. Men with cardiovascular problems linked to low levels of arginine and, consequently, NO, are more likely to suffer from ED and infertility. In fact, an erection requires NO to act on the smooth muscles of the blood vessels that fill the corpora cavernosa. According to some research, supplementation of Arginine combined with other vasodilators, antioxidants and anti-inflammatories, proved useful in about 92% of the male infertility cases analyzed. Stress can also reduce arginine production with negative reproductive effects, so overly stressed men can benefit from supplements containing this amino acid. Women can also use L-arginine-based products: doctors often prescribe topical creams containing arginine to manage small intimate problems (poor lubrication, irritation ...) as it improves circulation in the external genitals. Furthermore, some studies suggest that the combined treatment of N-acetyl cysteine (NAC) and L-arginine helps to naturally balance the hormonal structure of women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and estrogenic imbalances, improving the sexual sphere. and fertility.
- Increased athletic performance and endurance during physical exercise: thanks to the vasodilatory properties that increase the flow of blood, a greater quantity of nutrients and oxygen reaches the muscles and joints. For athletes, this allows for greater endurance during intense physical exertion and workouts. A greater transport of oxygen and nutrients is also essential in the recovery processes, favoring the restoration and formation of new muscle tissue. Good circulation also results in heat, beneficial for damaged joints, which radiates to the hands and feet. This is especially important for those with circulatory problems caused by poor limb supply, arthritis, or diabetes. In patients suffering from intermittent claudication (narrowing of the vessels in the lower limbs due to fat deposits), taking arginine supplements improves endurance by increasing the distance traveled without muscle pain. At the hormonal level, arginine induces the secretion of somatotropic hormone (or growth hormone, GH) which stimulates the development of cell mass and the use of adipose tissue for pro-energetic purposes; this was observed not only in sportsmen but also in sarcopenic, defunct or elderly patients in hospitalization.
- Immunostimulating properties: Low levels of arginine have been found in some immunosuppressed, traumatized or cancer patients. Arginine helps to stimulate the differentiation and activity of cytotoxic T lymphocytes and Natural Killer (NK) cells, the cells of the immune system that first intervene to defend the body from attacks by pathogens such as bacteria and viruses or from the formation of neoplastic cells. The use of supplements based on L-arginine, in combination with those based on omega-3 fish, has proved particularly useful in immunosuppressed subjects (such as HIV patients, cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy and transplant patients ) to improve the immunological structure, reducing recovery times.
- Diabetes therapy support: arginine improves glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity, allowing cells (especially those of the brain, liver and muscle tissue) to store larger quantities of this sugar in them for use as an energy source. In this way, blood sugar (ie the concentration of glucose circulating in the blood) is kept under control. Arginine works by counteracting high oxidative stress in diabetic patients, preserving the functionality and vitality of the pancreatic cells that produce insulin.
- Improve memory skills by fighting dementia: Maintaining normal NO levels by arginine is particularly important for a good memory. With aging, the production of arginine physiologically decreases and, consequently, of NO, therefore L-arginine supplements they are a great help for older people, especially when they start showing signs of senile dementia.
- Hair health: arginine seems to promote hair regrowth together with other amino acids such as cysteine, lysine and methionine. In fact, hair is mainly made up of keratin and collagen, two proteins which, in order to be synthesized, need precisely these amino acids in their structure. Arginine, in particular, thanks to the production of NO, improves blood circulation in the scalp, up to the follicles, providing nutrients and counteracting free radicals that are also formed as a result of pollution.
What happens in arginine deficiency?
Dal momento che l’arginina viene prodotta dall’organismo, in condizioni di salute, la carenza di tale amminoacido è abbastanza rara.
Tuttavia, come descritto nel paragrafo precedente, vi sono alcune condizioni, patologiche e non, che possono indurre una vera e propria carenza di arginina e che richiedono pertanto un’adeguata supplementazione.
Symptoms of arginine deficiency include: feeling fatigued, changes in sleep quality, and difficulty concentrating. The most serious symptoms are associated with pathologies that depend on the consequent levels of NO and molecules controlled by arginine.
In particular, L-arginine-based supplements are indicated for the following pathologies: hypertension; preeclampsia (increased blood pressure in pregnancy); congestive heart failure and cardiovascular problems; infertility and erectile dysfunction; cold hands and feet (even in summer); senile dementia.
What is the right dosage?
Finding the right dosage of L-arginine is difficult, precisely because it is not an essential amino acid. The integration must be decided together with the doctor and / or pharmacist and is indicated only for those who have a deficit or there is the need to increase its share (sports, cardiovascular and andrological diseases ...).
In fact, although arginine is produced by the body and taken from the diet, excessive consumption or supplementation can give important side effects. The dosages used are different and vary according to the needs of the people and the related problems to be treated; they are between 3 and 20 grams per day, divided into several assumptions.
It should be taken with main meals or within an hour and a half, unless otherwise prescribed. It is important to remember that taking L-arginine on an empty stomach has laxative effects.
For sportsmen and bodybuilders the recommended dosage is 3 grams and the intake takes place before training or night rest. To boost the immune system, a dose of 0.5 grams per 10kg of weight is recommended.
For a healthy adult aiming to prevent inflammation and maintain good circulation, the recommended daily allowance is 1 gram.
For diseases such as erectile dysfunction the maximum dosage is 5 grams / day while for cardiovascular problems it can be up to 10 or 20 grams per day.
Overdose, contraindications and precautions
L-arginine supplements are safe and generally well tolerated, and side effects are quite rare.
However, when taking dosages greater than 15 grams / day, symptoms may occur such as: cramp-like abdominal pain; allergic reactions (due to an excess of NO); stomach acid; nausea, vomiting and diarrhea.
More rarely, headache and hypotension may occur due to the vasodilating effects of arginine and increased blood sugar; these effects are related to the parenteral administration of L-arginine in the hospital setting.
L-arginine supplements are contraindicated in pregnant and lactating women due to lack of supporting scientific evidence, and in cases of amino acid hypersensitivity, liver and kidney insufficiency and genetic arginine disorder syndromes.
In case of liver and kidney diseases, arginine intake must be done under strict medical supervision.
Special precautions should be taken in patients with a history of myocardial infarction who should avoid high doses of L-arginine as excessive NO levels can have adverse effects on the heart.
Arginine also may increase the risk of bleeding in those who suffer from clotting problems or who are taking antiplatelet medications such as warfarin or blood-thinning supplements such as ginko biloba, garlic, and dwarf palm. Finally, arginine should not be administered to those prone to repeated viral infections by Herpes Simplex (cold sores and genital) and Herpes Zoster (known as Shingles) as this amino acid, being also present in proteins. of viruses, it could favor episodes of reactivation of the viral strain. Conversely, administration of the amino acid lysine improves the control of such infections.
Drug interactions
Beware of concomitant use of drugs as arginine can alter the pharmacokinetic properties of the following drugs leading also to a summation of effects:
- NSAIDs (Non Steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs), antiplatelet agents and anticoagulants due to the increased risk of bleeding;
- Antihypertensives: the co-administration of L-arginine causes excessive vasodilation with a drastic drop in blood pressure;
- Oral hypoglycemic agents and insulin: in case of hypoglycemia induced by the administration of insulin and oral hypoglycemic drugs (for example metformin) or fasting in diabetic patients, arginine stimulates gluconeogenesis or the synthesis of glucose and its release in the blood, reducing the effectiveness of antidiabetic therapy.
- Contraceptives and hormone-based therapies (estrogen and progestogen) that alter the effects of arginine on growth hormone, glucagon and insulin;
- Proton pump inhibitor antacids and H2 antihistamines: Arginine in high doses can increase gastric acidity by reducing the action of these drugs;
- Diuretics and ACE inhibitors: these drugs can cause an increase in potassium levels in the blood (hyperkalaemia) therefore careful monitoring of potassium is required in case of co-administration of L-arginine;
- Phosphodiesterase 5 (PDE5) inhibitors used in the treatment of erectile dysfunction (Sildenafil-Viagra, Tadalafil-Cialis, Verdenafil-Levitra): co-administration of Arginine may give a summing effect in the production of NO in the blood vessels of the penis with excessive vasodilatory action. In fact, erectile dysfunction drugs act differently than arginine as they block the PDE5 enzyme that would otherwise destroy NO. Arginine, on the other hand, enhances the action of NO towards the smooth muscle that lines the blood vessels of the corpora cavernosa. With both types of substances, the blood vessels in the penis dilate and an erection occurs. A recent 2019 study in ED patients showed that combining Viagra every other day with L-arginine on a daily basis is more effective. However, in order to avoid excessive effects, it is advisable to consult with your doctor.
Where do you buy L-arginine supplements?
L-arginine supplements are mostly sold in tablet and powder form, in some cases in topical creams and ointments or in hair products. In the hospital setting it is also available in the form of an infusion.
The supplements can be based on L-arginine alone or in combination with other amino acids, vitamins and minerals. It is possible to buy them in pharmacies, parapharmacies or online and are easily available as they do not require a prescription. In case of doubts, pharmacological therapies in progress or pathologies it is advisable to seek advice from your doctor or pharmacist.
At our site (https://www.biolineintegratori.com/) you can buy different L-Arginine supplements according to your needs. The company Bioline in fact offers 4 different products in tablets or powder with the following formulations:
👉 Is it possible to buy Arginine supplements afterwards?
Arginine supplements (Italian 100%) can be purchased at BiolineIntegratori.com. The available products are:
ARGININA Tab (compresse) —> Check the price
ARGINOX New, Stack di Arginina (compresse) —> Check the price
ARGININA AKG (polvere o compresse) —> Check the price
👉 What are the benefits of Arginine?
Arginine has:
- Anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties;
- Protective properties of the cardiovascular system;
- Healing properties of wounds;
- Supportive properties in the treatment of impotence and erectile dysfunction in men and male and female infertility;
- Supportive properties for increasing athletic performance and endurance during exercise;
- Immunostimulating properties;
- Supportive properties for diabetes therapy;
- Supportive properties of mnemonic abilities in fighting dementia;
- Supporting properties for hair health;
👉 What does an Arginine deficiency entail?
Since Arginine is produced independently by our body, its deficiency is quite rare.
However, there are some pathologies (listed in this article) that can lead to a lack of Arginine and therefore require the use of a supplement based on it.
Symptoms related to arginine deficiency include: fatigue, decreased sleep quality and difficulty concentrating.


Interesting thanks for the depth and care of the explanation.
Interessante spiegazione, e non sapevo servisse per la disfunzione eretiile ,fertilità e che fosse immunostimolante! Poiche sono ummunidepresso da oltre 12 anni per cure di un L non H, chiedevo che confezione potrei acquistare??
Giorgio
Gentile Giorgio, grazie per il suo commento. L’arginina ha davvero tante proprietà interessanti, come riportato nel testo. Questo è il link al prodotto a base di arginina: https://www.biolineintegratori.com/arginina-integratore/
Ho. Mio. Marito. Che. Soffre. Di. Depressione. I. Farmaci. Che. Assume. Le. Anno. Causato. Una. Disfunzione. Erettile. Sono. Costernato. E. Benefica. La. Arginina. Per. Il. Problema
Gentile Marisa grazie per la sua testimonianza. L’arginina è nota per il suo effetto sul monossido di azoto e quindi sulla vasodilatazione. Saluti
Volevo chiedere se prendo un grammo solo x dirmire… ma tutte le sere.. x integrare quelle che prendo prima del allenamento puo andar bene? Mi alleno 3 volte a settinana.. grazie..
Gentile Giovanni, può utilizzare il prodotto tutti i giorni alla dose riportata in etichetta, ovvero 2 compresse al giorno. Eventualmente può assumere 1 compressa tutte le sere e aggiungere 1 compressa prima dell’allenamento. Per ulteriori info può contattarci telefonicamente allo 0425940505. Saluti