Erectile dysfunction is one of the main urogenital pathologies of the male patient: a summary of the causes and risk factors.
Erectile dysfunction (ED) and benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) are the two main urogenital pathologies of the adult male patient and the elderly.
ED is a common problem affecting the 52% of men between 40 and 70, according to the American epidemiological study Massachussetts Male Aging Study, but it is only addressed by the 10% of those who suffer from it.
Erectile dysfunction is the inability of the male to achieve or maintain an erection sufficient to lead a satisfactory sexual intercourse.
THE erectile dysfunction problems they can compromise marital or sexual relations in progress and be the cause of unconsummated marriages and sterility, so it is important to face them and resolve them with appropriate therapies.
There are many treatments to deal with the problem, but the first step is to identify the origin of the dysfunction, or to define a cause.
The origin of the dysfunction can be of a psychological nature (eg: performance anxiety) or organic (eg: physical trauma to the genitals).
Usually, when there is a sudden onset, in the absence of comorbidities or trauma, associated with the presence of spontaneous morning erections, a social or psychological origin is more likely, while when the onset is gradual and progressive it is very likely that there is an organic cause behind erectile dysfunction.
Between drug treatments available phosphodiesterase 5 (PDE5) inhibitors such as sildenafil (Viagra®), tadalafil (Cialis®), vardenafil (Levitra®) and avanafil (Spedra®) are the most commonly used drugs.
These drugs must be taken under strict medical supervision and are not free from important side effects, they can be purchased at the pharmacy by showing a medical prescription.
Other remedies are food supplements based on the amino acid arginine, a precursor of nitrogen monoxide (NO), a powerful vasodilating agent that promotes erection.
In addition to arginine, other NO precursors are the amino acid citrulline or arginine alpha-ketoglutarate (AKG), commercially available in tablets or water dispersible powder.
However, it should be known that drugs and food supplements have no aphrodisiac effect, as is often believed by taking the well-known blue pill (Viagra®); their effectiveness must be accompanied by sexual stimulation and mental arousal.
What are the causes of erectile dysfunction?
The causes of erectile dysfunction they are different and very personal.
We will try to understand what they are in detail and how to act in the right way.
Causes of a psychological nature
Among the most common causes of nature psychological of erectile dysfunction there is performance anxiety, which determines an inhibitory effect on erection and is very frequent among young people in their first sexual experiences.
The emotional and affective involvement towards the partner plays a central role, since individuals who are unable to have an erective reaction with a partner, can safely end a satisfying sexual relationship with others.
Erectile dysfunction can be secondary to other psychiatric conditions such as anxiety and depression, and is resolved by treating the primary disorder.
However, many antidepressant and antipsychotic drugs negatively affect the ability to have an erection and therefore sexual performance.
Erectile dysfunction, due to psychological causes, is not a permanent condition.
The presence of erection with autoeroticism and involuntary morning erection rule out an organic cause.
Organic causes
The presence of organic causes underlying erectile dysfunction must be diagnosed by the doctor after excluding all possible psychological causes.
The pathogenesis of ED can be classified as follows:
- Vascular: vascular endothelium dysfunction;
- Endocrine: hypogonadism, hyperprolactinemia, Cushing's syndrome, somatotropin deficiency;
- Neurological: Parkinson's, Alzheimer's, spinal trauma, peripheral neuropathy (diabetes);
- Medical interventions: radical prostatectomy, cystectomy, radiotherapy for prostate cancer;
- Drugs and substances of abuse: cortisone, psychotropic drugs, antihypertensives; alcohol and cannabis cause increased sexual desire, but decrease sexual performance (duration and maintenance of an erection).
Risk factors
They were finally recognized numerous risk factors which increase the likelihood of erectile dysfunction including age, smoking, chronic alcohol and drug use, lack of exercise, hypercholesterolemia, obesity and diabetes.
Since the dilation of the blood vessels inside the corpora cavernosa of the penis is the mechanism underlying the erection, dysfunctions of the vascular endothelium cause a reduction in the release of nitric oxide (NO), a substance with a powerful vasodilating action.
Atherosclerosis is a serious disease affecting the walls of blood vessels, and represents the first risk factor for diseases that are widespread in industrialized countries such as heart attack or stroke.
At the base of the atherosclerotic process there is always an endothelial dysfunction, so there is a close correlation between the risk factors of atherosclerosis and those of erectile dysfunction.
Physiology: how does an erection happen?
Penile innervation includes both autonomic and somatic nerves; nitric oxide (NO) is the main chemical mediator of erection and is released from the endothelium (blood vessel wall) and nerves as a result of mental arousal.
NO acts inside the smooth muscle cells of the arterioles of the corpora cavernosa of the penis, stimulating the production of cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP), responsible for smooth muscle relaxation and therefore vasodilation.
The vasodilation of the arterioles induces both an increase in blood flow to the penis and compression of the veins, occluding the outflow of venous blood; therefore the considerable increase in blood pressure inside the corpora cavernosa of the penis causes an erection.
Phosphodiesterases, in particular those of type 5 (PDE5), are enzymes that inhibit the action of cGMP causing the loss of erection.
PDE5 inhibitors (such as Viagra®) and similar drugs block the action of PDE5, increasing survival and therefore the vasodilating action of cGMP.
Fundamental role of nitrogen monoxide (NO)
NO is a fairly ubiquitous molecule in the body, and is produced starting from the amino acid arginine through a biochemical reaction catalyzed by the enzyme nitric oxide synthetase (NOS) (Fig. 1).
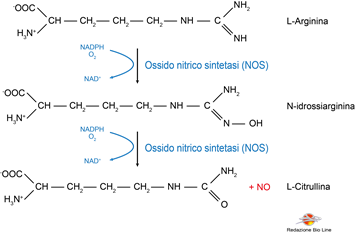
Fig. 1 - Synthesis of NO starting from arginine
In the body, NO performs numerous functions as a chemical messenger: its role is recognized in the brain (learning and memory), gastrointestinal (modulation of secretion and motility), respiratory (control of the smooth muscles of the bronchi), renal (regulation blood flow to the kidney).
However, its pre-eminent role is carried out at the level of the cardiovascular system by causing the relaxation of the smooth muscle of the arteries (vasodilation), reduction of platelet aggregation and the adhesion of leukocytes to the vessel walls.
The release of NO by the endothelial cells of the penile arteries causes an erection.
After the NO has acted it is transformed into a series of derivatives such as nitrites and nitrates which are eliminated from the body through the urine.

